Usefulness of the MRI for the differential diagnosis of the pleural lesion including malignant pleural mesothelioma
MRI (DWI) can assess pleural lesions including malignant pleural mesothelioma as malignant or benign.
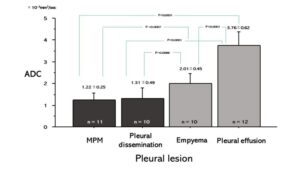 Fig. 21 Differences of ADC among pleural lesions Mean ADCs were 1.22 ± 0.25×10-3mm2/sec in MPM, 1.31±0.49×10-3mm2/sec in pleural dissemination, 2.01±0.45×10-3mm2/sec in empyema, and 3.76±0.62×10-3mm2/sec on pleural effusion. ADC of MPM was significantly lower than that of empyema (P =0.0007) or pleural effusion (P<0.0001). ADC of pleural dissemination was significantly lower than that of empyema (P=0.0086) or pleural effusion (P<0.0001). Usuda K, et al. Cancers 2019;11(6).
Fig. 21 Differences of ADC among pleural lesions Mean ADCs were 1.22 ± 0.25×10-3mm2/sec in MPM, 1.31±0.49×10-3mm2/sec in pleural dissemination, 2.01±0.45×10-3mm2/sec in empyema, and 3.76±0.62×10-3mm2/sec on pleural effusion. ADC of MPM was significantly lower than that of empyema (P =0.0007) or pleural effusion (P<0.0001). ADC of pleural dissemination was significantly lower than that of empyema (P=0.0086) or pleural effusion (P<0.0001). Usuda K, et al. Cancers 2019;11(6).
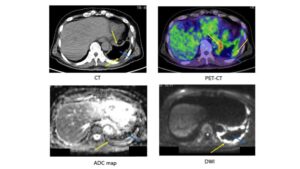
Fig. 22 Case 1 Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) MPM (cT4N2M0). The yellow arrow shows MPM. The blue arrow shows pleural effusion. ADC of MPM was 0.84 x10-3 mm2/sec (positive) and ADC of pleural fluid was 3.95 x10-3 mm2/sec (negative). FDG-PET/CT showed partial accumulation (SUVmax: 12.39) of FDG on the MPM. Usuda K, et al. Cancers. 2019;11(6).
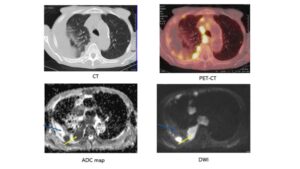 Fig. 23 Case 2 Pleural dissemination of lung cancer Pleural dissemination of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. The yellow arrow shows pleural dissemination. The blue arrow shows pleural fluid. ADC of pleural dissemination was 0.67 x10-3 mm2/sec (positive) and ADC of pleural fluid was 3.03 x10-3 mm2/sec (negative). FDG-PET/CT showed scattered accumulation (SUVmax: 14.7) of FDG on the pleural dissemination. Usuda K, et al. Cancers. 2019;11(6).
Fig. 23 Case 2 Pleural dissemination of lung cancer Pleural dissemination of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. The yellow arrow shows pleural dissemination. The blue arrow shows pleural fluid. ADC of pleural dissemination was 0.67 x10-3 mm2/sec (positive) and ADC of pleural fluid was 3.03 x10-3 mm2/sec (negative). FDG-PET/CT showed scattered accumulation (SUVmax: 14.7) of FDG on the pleural dissemination. Usuda K, et al. Cancers. 2019;11(6).
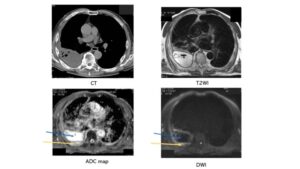 Fig. 24 Case 3 Empyema A 70-year-old male with right empyema. The yellow arrow shows pleura. The blue arrow shows pleural fluid. ADC of Pleural thickness was 1.82 x10-3 mm2/sec (negative) and ADC of pleural fluid was 3.95 x10-3 mm2/sec (negative). Usuda K, et al. Cancers. 2019;11(6).
Fig. 24 Case 3 Empyema A 70-year-old male with right empyema. The yellow arrow shows pleura. The blue arrow shows pleural fluid. ADC of Pleural thickness was 1.82 x10-3 mm2/sec (negative) and ADC of pleural fluid was 3.95 x10-3 mm2/sec (negative). Usuda K, et al. Cancers. 2019;11(6).
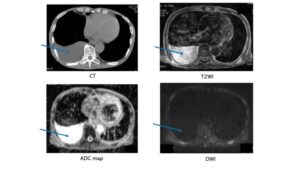 Fig. 25 Case 4 Pleural effusion A 79-year-old male with right pleural effusion. The blue arrow shows pleural fluid. Pleural effusion was not seen in DWI. ADC of pleural fluid was 4.02 x10-3 mm2/sec (negative). Usuda K, et al. Cancers. 2019;11(6).
Fig. 25 Case 4 Pleural effusion A 79-year-old male with right pleural effusion. The blue arrow shows pleural fluid. Pleural effusion was not seen in DWI. ADC of pleural fluid was 4.02 x10-3 mm2/sec (negative). Usuda K, et al. Cancers. 2019;11(6).
Usuda K, et al. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Can Differentiate between Malignant and Benign Pleural Diseases Cancers. 2019 Jun 12;11(6). 811. doi: 10.3390/cancers11060811.
Pessôa, FM, et al. Applications of magnetic resonance imaging of the thorax in pleural diseases: A state-of-the-art review. Lung 2016, 194, 501–509.