PET-CT (FDG-PET/CT: 18-fluoro-2-deoxy-glucose positron emission tomography / computed tomography) has been the primary method for the diagnosing and staging of metastatic lesions according to the cancer screening protocols of Japan. When getting a PET-CT, FDG is able to show the glucose metabolism of the target lesion. The fact that PET-CT is not only more expensive than MRI and you will also need a contrast medium of FDG (a radioisotope) but the patient will also be exposed to harmful radiation in the process. Naturally FDG shows glucose metabolism of the lesion. PET-CT is not a perfect examination because of false negatives with small size tumors or tumors with little glucose metabolism, and it will also show a false positive for inflammatory lesions. PET-CT needs the injection of the radioisotope, the cost of the examination is approximately ¥30,000 (30,000 JPY) with a 30% deductible. Whereas an MRI is economical at approximately ¥6,000 (6,000 JPY), 1/5 the cost of PET-CT with a 30% deductible (Table 1).
Table 1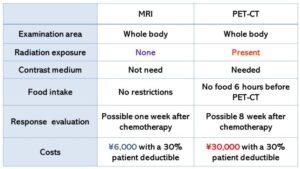
A. Medical costs of examinations in Japan
Recently the medical costs of healthcare have been increasing dramatically. As of 2023 the Medical costs for the following medical examinations in Japan are as follows; ¥10,000 (10,000 JPY) for CT, ¥13,300 (13,300 JPY) for MRI of 1.5T, and ¥16,000 (16,000 JPY) for MRI of 3T (Table 2). An additional cost of ¥5,000 (5,000 JPY) is sometimes needed for the contrast medium in CT or MRI. The other medical costs include ¥22,000 (22,200 JPY) for bone scintigraphy and ¥18,000 (18,000 JPY) for gallium scintigraphy. Furthermore, the cost of a positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) using FDG is ¥86,250 (86,250 JPY), which is considerably more expensive. The cost of an MRI is cheaper, only 15- 20% of that of PET-CT. MRIs can reduce the costs for hospitals and patients by 84% compared to PET-CT while still providing the same or better results、according to my research.
Usuda K, et al. Economic Benefits and Diagnostic Quality of Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Primary Lung cancer. Ann Thoracic Cardiovasc Surgery 2017; 23 (6), 275-280.
Here is a diagnostic performance of MRI when compared to that of PET-CT where the results are the same or better. We believe this book will have a positive effect globally in terms of the acceptance of using MRI in evaluating lung cancer, pulmonary nodule/mass and thoracic neoplasm.
Table 2 Medical costs of examinations in Japan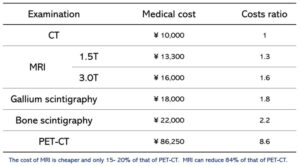
- Usefulness of MRI (Table 3)

The MR diffusion weighted image (diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging: DWI) is used to depict the suppressed region of the diffusion phenomenon (Brownian movement of the water molecule), and the following efficacy has been proven.
Generally, cell density of malignant tumors is higher and there is a decrease in movement of water molecules of the malignant tumors compared to benign lesions.
Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) means a standard value of diffusion which is useful for discriminating malignancy from benignity in humans. Usually, a malignant tumor shows a low value of 0.8 to 1.4 x 10-3mm2/sec. On the other hand, it is known that ADC of benign lesions are more than 2.0 x 10-3mm2/sec. In this book, a lot of the ADC data points are presented as diagnostic values.
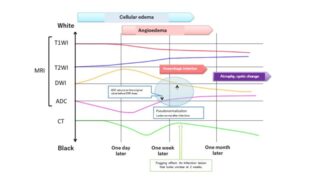
The MR diffusion-weighted image (DWI) was applied first in the cranial nerve region and has been primarily used to discover acute ischemic strokes. In common MRIs, only a cerebral infarction that has passed is depicted as white, but a new cerebral infarction is not detected. However, with DWIs, a new cerebral infarction is depicted 1 hour after its onset. Within 4.5 hours after the onset of a new cerebral infarction, thrombus dissolving drugs are administered to the patient according to the supporting stroke treatment guidelines 2015 (Table 3). DWI became an established examination for prostate cancer in the treatment guidelines of prostate cancer 2015 (Table 3). Small early prostate cancers in the inner gland are able to be identified using DWI. The characteristic of DWI is highly sensitive, and it came to be used to detect cancers of the transitional regions that may be overlooked by a biopsy. DWI has a much lower risk factor than a biopsy and is able to detect a cancerous lesion with incredible sensitivity.