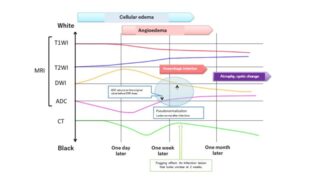
The research group of Dr. Taro Takahara and Professor Dr. Yutaka Imai of Tokai University have developed an epoch-making method, diffusion-weighted whole-body imaging with background suppression (DWIBS) which searches a whole body by one MRI (DWI) exploration in 2004. Diagnostic ability of PET-CT and that of DWIBS are similar. Some diagnostic abilities are better in DWIBS in PET-CT, other better in PET-CT than DWIBS. However, patients cannot receive PET-CT more than once a year in health insurance because it is expensive and approximately 30,000 yen in a 30% burden. On the other hand, DWIBS is a MR imaging that we do not need a contrast medium. Therefore, a patient can have it one to three months under health insurance.
We presented good points of DWIBS compared with PET-CT. Also, we showed a comparison between DWIBS and PET-CT.
Also, we showed a comparison between DWIBS and PET-CT.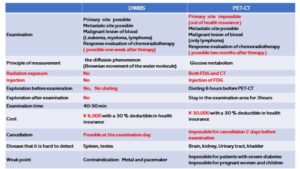
We reported that DWIBS could detect recurrence and metastasis with a better accuracy after surgery of lung cancer.
Usuda K, et al. Diffusion‐weighted whole‐body imaging with background suppression (DWIBS) is effective and economical for detection of metastasis or recurrence of lung cancer. Thoracic cancer 2021:12 (5):676 – 684. doi:10.1111/1759-7714.13820
Background: Diffusion-weighted whole-body imaging with background suppression (DWIBS) is used for the diagnosis and staging of cancers. The medical cost of an MR examination including DWIBS is $123, which is 80% less expensive than the cost ($798) of F18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (FDG-PET/CT) examination. Methods: This study examined the efficacy of DWIBS for relapses after lung cancer resection. A total of 55 patients who had pulmonary resection of lung cancer, postoperative computed tomography (CT) every six months, and DWIBS and FDG-PET/CT (every year) were enrolled in this study. If a metastatic lesion was detected on CT scan, DWIBS and FDG-PET/CT were also used. Results: A total of 55 patients who underwent pulmonary resections for lung cancer, and had CT, DWIBS and FDG-PET/CT examination during follow-up after pulmonary resection were enrolled in this study. Lung cancer in 32 patients relapsed. Postoperative radiographic examinations revealed pulmonary metastases in 17 patients, bone metastases in seven, liver metastases in five, lymph node metastases in five, pleural metastases in four, metastases to the chest wall in two, brain metastases in two, adrenal gland metastasis in one, and renal metastasis in one. The mean apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value of the relapse was 0.9 to 1.70 × 10−3 mm2/s. The accuracy 0.98 (54/55) of DWIBS for detecting multiple metastatic lesions was likely to be higher than 0.94 (52/55) of CT or 0.94 (52/55) of FDG-PET/CT, but there were no significant differences. Conclusions: DWIBS can detect multiple metastatic lesions throughout the entire body and differentiate malignancy from benignity in only one examination. DWIBS has benefits of diagnostic accuracy and is less expensive in medical costs for the detection of a relapse. DWIBS could potentially replace FDG-PET/CT after lung cancer resection.
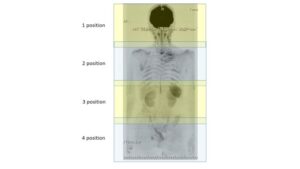 Fig. For DWIBS, 4-5 positions were needed for each patient to scan the whole body. Each position needs 4 minutes and 4-5 positions were repeated and T1WI of anatomical images is added for superposition of the images.
Fig. For DWIBS, 4-5 positions were needed for each patient to scan the whole body. Each position needs 4 minutes and 4-5 positions were repeated and T1WI of anatomical images is added for superposition of the images.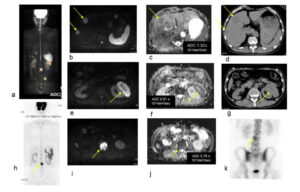 Fig. Case1. LCNEC pT2aN0M0. (a): Whole body imaging of DWIBS (a) show metastases to liver, kidney, vertebra and ilium. Multiple liver metastases were presented in DWIBS (b), ADC map (c), and CT (d). The ADC of a liver metastasis was 1.32×10−3mm2/sec (c). Left renal metastasis was presented in DWIBS (e), ADC map (f), and CT (g). The ADC of the left renal metastasis was 0.91×10−3mm2/sec (f). Metastases to lumbar vertebra is shown in DWIBS (h,i) and in bone scintigraphy (k). The ADC of the lumbar vertebra metastasis was 0.76×10−3mm2/sec (j). DWIBS showed the lumbar vertebra metastasis more clearly than bone scintigraphy did.
Fig. Case1. LCNEC pT2aN0M0. (a): Whole body imaging of DWIBS (a) show metastases to liver, kidney, vertebra and ilium. Multiple liver metastases were presented in DWIBS (b), ADC map (c), and CT (d). The ADC of a liver metastasis was 1.32×10−3mm2/sec (c). Left renal metastasis was presented in DWIBS (e), ADC map (f), and CT (g). The ADC of the left renal metastasis was 0.91×10−3mm2/sec (f). Metastases to lumbar vertebra is shown in DWIBS (h,i) and in bone scintigraphy (k). The ADC of the lumbar vertebra metastasis was 0.76×10−3mm2/sec (j). DWIBS showed the lumbar vertebra metastasis more clearly than bone scintigraphy did.
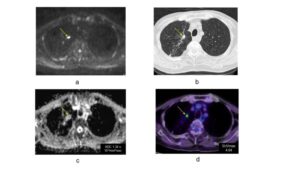 Fig. Case 2. Adenocarcinoma, pT2aN0M0 Pulmonary metastasis was presented in DWIBS (a), CT (b) and FDG-PET/CT (d). The ADC of pulmonary metastasis in ADC map was 1.34 x 10-3mm2/sec (c). The SUVmax of the pulmonary metastasis in FDG-PET/CT was 4.04 (d).
Fig. Case 2. Adenocarcinoma, pT2aN0M0 Pulmonary metastasis was presented in DWIBS (a), CT (b) and FDG-PET/CT (d). The ADC of pulmonary metastasis in ADC map was 1.34 x 10-3mm2/sec (c). The SUVmax of the pulmonary metastasis in FDG-PET/CT was 4.04 (d).
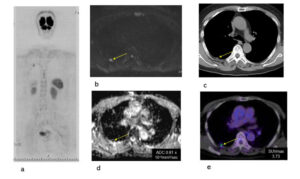 Fig. Case 3. Adenocarcinoma, pT2aN0M0. Pleural metastasis was presented in DWIBS (a, b), CT (c) and FDG-PET/CT (e). The ADC of the pleural metastasis in ADC map was 0.81 x 10-3mm2/sec (d). The SUV max of the pleural metastasis in FDG-PET/CT was 3.73 (e). It was diagnosed as a metastasis from lung cancer by resection under thoracotomy. The tiny metastatic lesion could be detected by DWIBS.
Fig. Case 3. Adenocarcinoma, pT2aN0M0. Pleural metastasis was presented in DWIBS (a, b), CT (c) and FDG-PET/CT (e). The ADC of the pleural metastasis in ADC map was 0.81 x 10-3mm2/sec (d). The SUV max of the pleural metastasis in FDG-PET/CT was 3.73 (e). It was diagnosed as a metastasis from lung cancer by resection under thoracotomy. The tiny metastatic lesion could be detected by DWIBS.
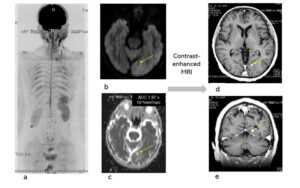 Fig. Case 4. Squamous cell carcinoma. pT3N0M0. Whole body imaging in DWIBS (a). Tiny brain metastasis was presented in DWIBS (b). The ADC of the brain metastasis in ADC map was 1.94x 10-3mm2/sec, and it was a false negative (c). Enhanced brain MRI was added to conform the brain metastasis. DWIBS could be useful to detect a brain metastasis. The DWIBS-enhanced lesion (ADC 2.04 x 10-3mm2/sec) at the level of rt. kidney, which was located in abdominal wall and had not changed for one year, was diagnosed a benign neurogenic tumor.
Fig. Case 4. Squamous cell carcinoma. pT3N0M0. Whole body imaging in DWIBS (a). Tiny brain metastasis was presented in DWIBS (b). The ADC of the brain metastasis in ADC map was 1.94x 10-3mm2/sec, and it was a false negative (c). Enhanced brain MRI was added to conform the brain metastasis. DWIBS could be useful to detect a brain metastasis. The DWIBS-enhanced lesion (ADC 2.04 x 10-3mm2/sec) at the level of rt. kidney, which was located in abdominal wall and had not changed for one year, was diagnosed a benign neurogenic tumor.